American imperialism map worksheet answers offer an invaluable resource for understanding the historical expansion of the United States. This comprehensive guide delves into the origins, motivations, and consequences of American imperialism, providing a detailed account of the territories acquired during this period and their lasting impact on the world stage.
Through a detailed map and insightful analysis, this worksheet illuminates the complex factors that drove American expansionism, including economic, political, and social forces. It also examines the positive and negative outcomes of imperialism, both for the United States and the territories it acquired.
Historical Context
American imperialism refers to the United States’ expansionist policies that led to the acquisition of territories beyond its original borders. The origins of American imperialism can be traced back to the 19th century, when the United States emerged as a global power following the Spanish-American War and the acquisition of territories such as Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines.
Timeline of Key Events and Acquisitions:
- 1803: Louisiana Purchase
- 1819: Florida Purchase
- 1845: Annexation of Texas
- 1846-1848: Mexican-American War and acquisition of California, Nevada, Utah, and parts of Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming
- 1853: Gadsden Purchase
- 1867: Alaska Purchase
- 1898: Spanish-American War and acquisition of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines
- 1899: Annexation of Hawaii
Geographic Expansion: American Imperialism Map Worksheet Answers
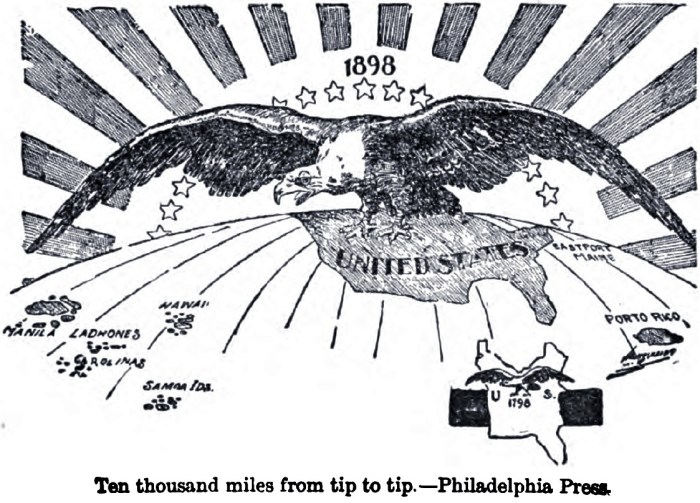
The United States expanded its territories primarily through the following methods:
- War:The United States acquired territories such as California and New Mexico through military conquest during the Mexican-American War.
- Purchase:The United States purchased territories such as Alaska and the Louisiana Territory from other nations.
- Annexation:The United States annexed territories such as Texas and Hawaii, which had previously been independent nations.
Map of Territories Acquired by the United States during its Imperialist Period:
The map should include the following territories:
- Louisiana Territory
- Florida
- Texas
- California
- Nevada
- Utah
- Arizona
- New Mexico
- Colorado
- Wyoming
- Alaska
- Puerto Rico
- Guam
- Philippines
- Hawaii
Motivations and Consequences
Economic Factors:
- Access to new markets for American goods
- Acquisition of natural resources, such as oil and minerals
Political Factors:
- Desire to expand American power and influence
- Belief in the superiority of American values and institutions
Social Factors:
- Nationalism and patriotism
- Belief in the “Manifest Destiny” of the United States to expand westward
Positive Consequences:
- Expansion of American territory and population
- Access to new resources and markets
- Spread of American values and institutions
Negative Consequences:
- Conflict with indigenous populations and other nations
- Exploitation of resources and people in acquired territories
- Spread of American imperialism and its negative effects on other nations
Legacy and Impact
The legacy of American imperialism is complex and far-reaching.
On the World Stage:
- Shaped international relations and global power dynamics
- Contributed to the rise of the United States as a global superpower
- Led to the spread of American values and institutions around the world
On the United States:
- Expanded the size and diversity of the American population
- Boosted the American economy
- Strengthened the American military
- Raised questions about the morality and legitimacy of American imperialism
FAQ Compilation
What were the key motivations behind American imperialism?
Economic expansion, political power, and social Darwinism were among the primary motivations driving American imperialism.
What were the consequences of American imperialism for the territories acquired?
The consequences varied depending on the territory, but often included political instability, economic dependency, and cultural assimilation.
How did American imperialism shape international relations?
American imperialism led to increased tensions with other world powers, particularly European colonial empires, and contributed to the rise of nationalism and anti-colonial movements.
