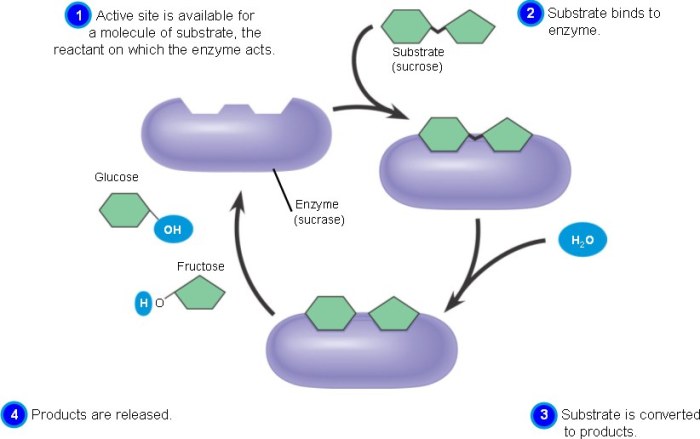
Match each description with the appropriate step in enzyme catalysis. Enzyme catalysis is a fascinating process that allows biochemical reactions to occur at rates that would otherwise be impossible. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, increasing the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
The process of enzyme catalysis involves several distinct steps, each of which plays a crucial role in the overall reaction.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the steps involved in enzyme catalysis, including enzyme-substrate binding, formation of the enzyme-substrate complex, the catalytic step, and product release. We will also discuss the factors that influence enzyme activity and the role of enzyme inhibitors.
Enzyme Catalysis: Match Each Description With The Appropriate Step In Enzyme Catalysis.
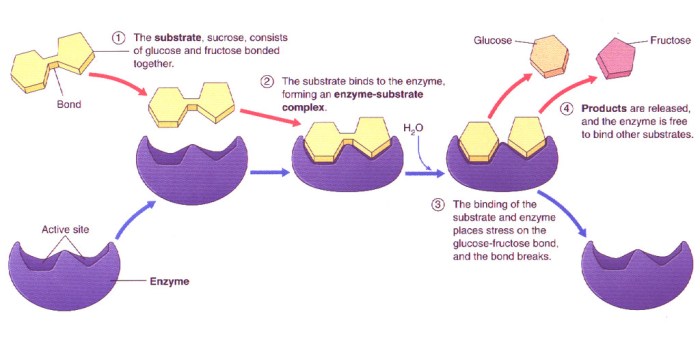
Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They play a crucial role in various biological processes, such as metabolism, digestion, and DNA replication. The mechanism of enzyme catalysis involves a series of steps, including enzyme-substrate binding, formation of enzyme-substrate complex, catalytic step, and product release.
Enzyme-Substrate Binding
The first step in enzyme catalysis is the binding of the enzyme to its substrate. Enzymes have specific active sites that are complementary to the substrate’s structure. The active site provides a favorable environment for the substrate to bind and undergo a chemical reaction.
- Induced fit model:The enzyme’s active site changes shape upon substrate binding to accommodate the substrate.
- Lock-and-key model:The enzyme’s active site is pre-formed and perfectly complementary to the substrate, like a lock and key.
Formation of Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Once the enzyme binds to the substrate, a complex is formed. This complex brings the substrate into close proximity with the enzyme’s catalytic site.
- Conformational changes:Substrate binding often induces conformational changes in the enzyme, bringing the catalytic residues into optimal positions.
- Stabilization of transition state:The enzyme-substrate complex stabilizes the transition state of the reaction, which is the high-energy intermediate state.
Catalytic Step, Match each description with the appropriate step in enzyme catalysis.
The catalytic step involves the chemical reaction that converts the substrate into products. Enzymes use various catalytic mechanisms to lower the activation energy of the reaction.
- Acid-base catalysis:Enzymes use proton donors or acceptors to facilitate proton transfer reactions.
- Coenzyme catalysis:Enzymes utilize coenzymes, such as NAD+ or FAD, to carry electrons or functional groups during the reaction.
- Metal ion catalysis:Metal ions, such as zinc or iron, participate in catalytic reactions by stabilizing charges or facilitating electron transfer.
Product Release
After the reaction is complete, the products are released from the enzyme. This allows the enzyme to bind to another substrate and repeat the catalytic cycle.
- Product inhibition:High concentrations of products can inhibit enzyme activity by competing with the substrate for binding to the active site.
- Enzyme turnover:The number of substrate molecules converted per unit time by a single enzyme molecule is known as enzyme turnover.
- Enzyme inhibitors:Inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and reduce their activity. They can be competitive, non-competitive, or uncompetitive.
Clarifying Questions
What is enzyme catalysis?
Enzyme catalysis is the process by which enzymes increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
What are the steps involved in enzyme catalysis?
The steps involved in enzyme catalysis include enzyme-substrate binding, formation of the enzyme-substrate complex, the catalytic step, and product release.
How do enzymes increase the rate of a reaction?
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and reduce their activity.